In today’s article, we are here to discuss the Genetically Modified Crops which is also known as GM Crops. It is the fasted methodology adopted by the farmer’s worldwide. In 2016, 95.6 million hectares Genetically modified crops were cultivated.
Genetically Modified Crops
What is Genetically Modified Crops (GM Crops)?
When we talk about genetically modified crops, we must begin by clarifying that all the plants that are grown today in the world have been modified by the man using different mechanisms that allow them to select characteristics according to their needs.
Initially, the improvement of the crops was carried out intuitively and based on the experience left by each harvest. By sowing and selecting seeds, man expanded the number of species cultivated and adapted to local conditions, to the uses and customs of each area. With time, the advance and development of human knowledge allowed to perfect agriculture.
At present, modern science offers new methods to obtain better varieties in less time and with greater short and long-term benefits. One of these tools is up to date biotechnology.
The improvement of plants thus became a process-oriented and without the intervention of chance. In this way, agriculture and the improvement of crops were transformed into activities based on scientific knowledge.
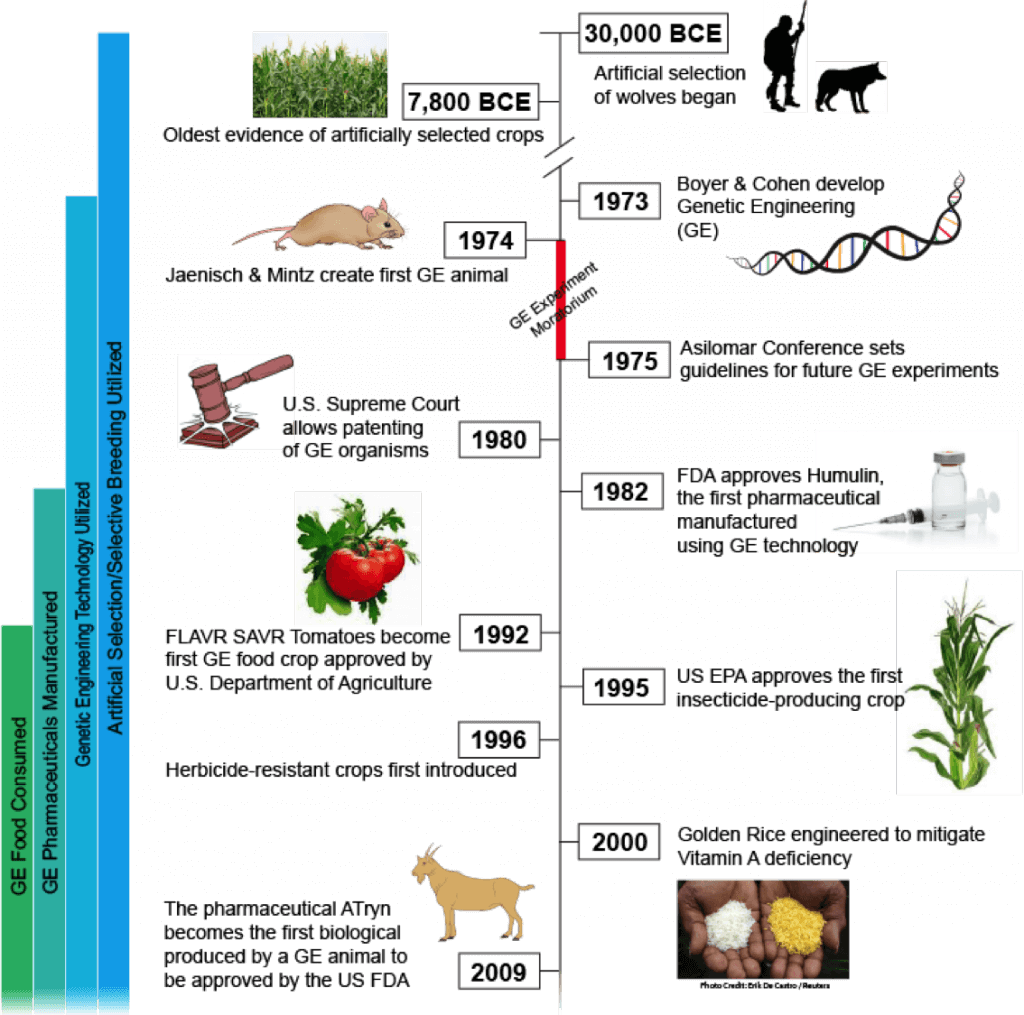
History of Genetically Modified Crops (GM Crops)
The genetically modified plants (GM) began to develop in the early eighties, as a result of the application of modern biotechnology. In 1875, a Hybrid cereal was found by crossing wheat and rye.
GM plants are those whose genetic information (genome) has been modified by genetic engineering, either to introduce one or several new genes or to modify the function of a gene itself.
As a result of this modification, GM plants show a new feature, for example, resist a pest or produce more proteins or vitamins. The development of GM plants is possible as a result of the sc
How Genetically Modified Crops Created?
All living organisms are made up of DNA, which in turn are organized into genes, which control all aspects of the life of organisms, including form, development, reproduction and the information necessary for a characteristic to be expressed.
Genetically modified plants are organisms to which a gene has been inserted in a stable form that gives them the desired characteristic. This is how, for example, BT crops (gene from Bacillus Thuriniensis) are those that have the characteristic of being resistant to some insects.
The modification of the plants is born from an identified need, for example, to mitigate problems such as weeds and pests that attack crops.
Identification and isolation of Genetically Modified Crops
The process of developing a genetically modified organism is done in the following steps:
In this stage, the problem or need is identified and the characteristic is determined (for example desired protein) for the solution thereof. After the gene of interest is located, it is isolated from the organism to multiply it and adapt it to the need or problem.
Genetically modified crops are necessary for food security?
Genetically modified crops capable of eliminating insect pests or tolerating herbicides have transformed the cultivation of soy, cotton, corn, and canola, which reduces costs and increases productivity, but the lack of knowledge hinders further improvements in performance, especially with new conditions climatic
Climate change will affect yields and product quality in a lot of ways, increasing temperatures will accelerate crop development and therefore limit yield potential, and in colder climates, higher temperatures could prolong the season. Of growth, for the most part in crops with indeterminate growth, such as cotton
Genetically modified crops make changes in agricultural management to assist plants an improved survive ecological changes
Even though it is true that these organisms should not be promoted as the only response to climate change, the truth is that they could be an important aid for humanity. Another example where genetically modified crops could be applied would be in the resistance to pests,
Despite the controversy, the fact is that genetically modified crops are safe, according to scientific studies that have been carried out for decades. And is that initiatives such as golden rice, which seeks to cure blindness in Asian children
As we see, genetically modified crops are positioned with great applications that we should not lose sight of in the future. Health, food or agriculture is three of the areas where biotechnology could be used, in order to get better our development.
Currently, the cultivation of genetically modified crops is distributed among 26 countries, of which 19 are in the process of development.
The industrialized countries cultivated the majority of GM plants, with the USA at the head, and that continues today as the largest producer. Since then, the developing countries have taken the lead in planting “biotech” crops, with Brazil allocating a larger area to this type of crops within this group.
Given that a greater number of countries in the southern hemisphere are adopting the use of this type of crops, and that the commercial cultivation of genetically modified rice is increasingly close, expect that trend to continue. In the European Union (EU), the cultivation of genetically modified plants began, and since then their use has been very limited.
At present, only the genetically modified MON810 corn variety is authorized for cultivation, while a much larger number of genetically modified species and varieties are authorized for use in human and animal feed, or for other industrial applications.
On the other hand, the marketing of genetically modified foods for human consumption in the EU is minimal, while its use in animal feed is substantial.
The scientific literature that addresses this topic is abundant and sometimes the results published on specific cases are contradictory, which highlights the need to continue researching thoroughly about the possible environmental impact of Genetically modified crops, in order to understand where the balance risk-benefit in each situation, for all time taking as reference the risks associated with the cultivation of conventional species.
Advantages of Genetically Modified Crops (GM Crops)
GM crops capable of eliminating insect pests or tolerating herbicides have transformed the cultivation of soy, cotton, corn, and canola, which reduces costs and increases productivity, but the lack of knowledge hinders further improvements in performance, in particular with new climatic conditions.
It is a tool that is available to the farmer which allows him to protect his crops, save costs and be friendlier to the environment.

